When a bearing fails, it indicates the ineffectiveness of the bearing motion. The machine shaft would
eventually fail without sufficient bearing action, resulting in machine damage and breakdowns. In this
article, FEIKEN Bearing would explain more to readers regarding the factors of bearing failure and
ineffectiveness.
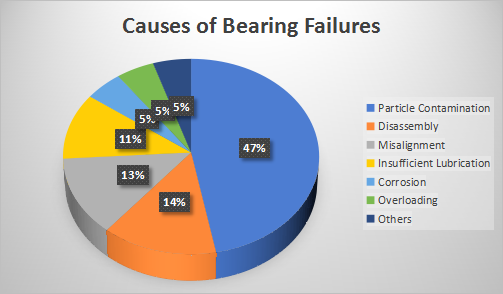
The above pie chart displays a better illustration of the statistics underlying common bearing failure
reasons. By learning from this article, readers are exposed to the knowledge of these potential problems and
may help to prevent bearing malfunctions.
Common Causes of Bearing Failure

Lubrication Failure
Improper lubrication is the main common cause of bearing failure. The factors of damaged bearings due to lubrication failure are such as improper lubricant used, lack of lubricant applied, or the bearing has been subjected to extreme temperatures that have caused the lubricant to deteriorate.
Misalignment
Apart from lubrication failures, bearing misalignment is the second most prevalent cause of early bearing failure. When the faces of the inner and outer rings are not parallel, rolling element bearings are misaligned. The inner ring on the shaft or the outer ring in the housing might be crooked.
Corrosion and Contamination
Contaminants in bearing components, such as dirt, sand, water, and chemical compounds, create a variety of problems. These contaminants reduce the flow of lubricant fluids, leading to bearing surface corrosion, disruption of the oil layer, and erosion, which would result in an increase in the friction on the bearing.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a condition where bearing surfaces or raceways have fractures, causing the removal of tiny pieces of bearing materials such as metal and other particles. If this fatigue continuously spreads, it can lead the bearing to failure and malfunction.
Aug 28,2023
